
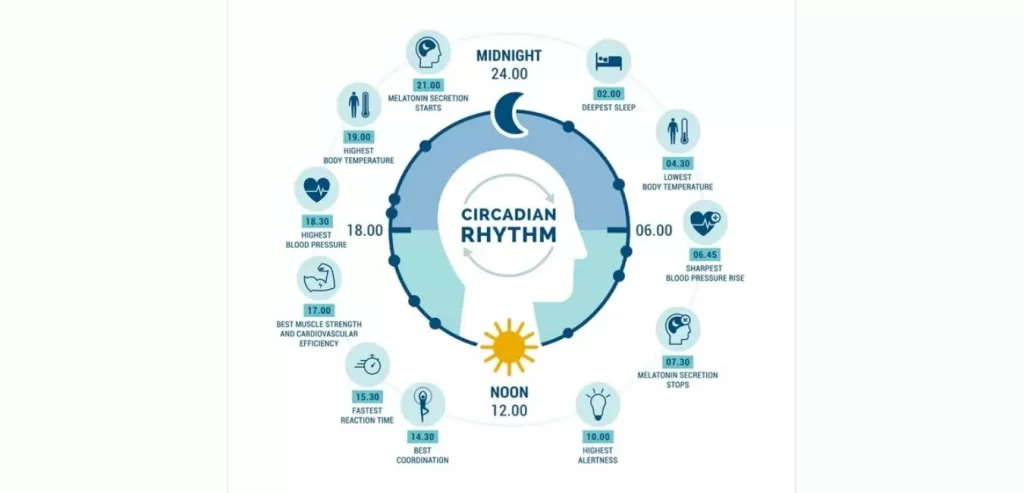
Circadian rhythm is an internal body clock that helps control your sleep and wake cycle. The natural body clock is influenced by environmental cues, primarily light. Depending on the environment, your brain sends signals to certain hormones, modifies your body temperature, and draws you to sleep. It also affects your sleep patterns as well as the way your body works, hormones, and eating habits. If these are out of sync, there are chances of health issues. So it is essential to keep this cycle in sync
How does it work?
The cells later export more signs to different segments of the brain that stimulate other functions that make you further tired or alert.
Hormones play a role: Hormones like melatonin and cortisol may enhance or decline as part of your natural body clock. Melatonin is a hormone that affects your sleep, and your body delivers more of it at night and suppresses it throughout the day. Cortisol can make you more alert, and your body generates more of it in the morning.
Other factors: Body temperature and metabolism are also part of your circadian rhythm. Your temperature reduces when you sleep and raises during awake hours. Additionally, your metabolism works at various standards during the day.
Your rhythm may alter based on your job hours, physical activity, and habits or lifestyle preferences.
Age is a different part that changes your circadian rhythm. Infants, teens, and adults all endure circadian rhythms uniquely.
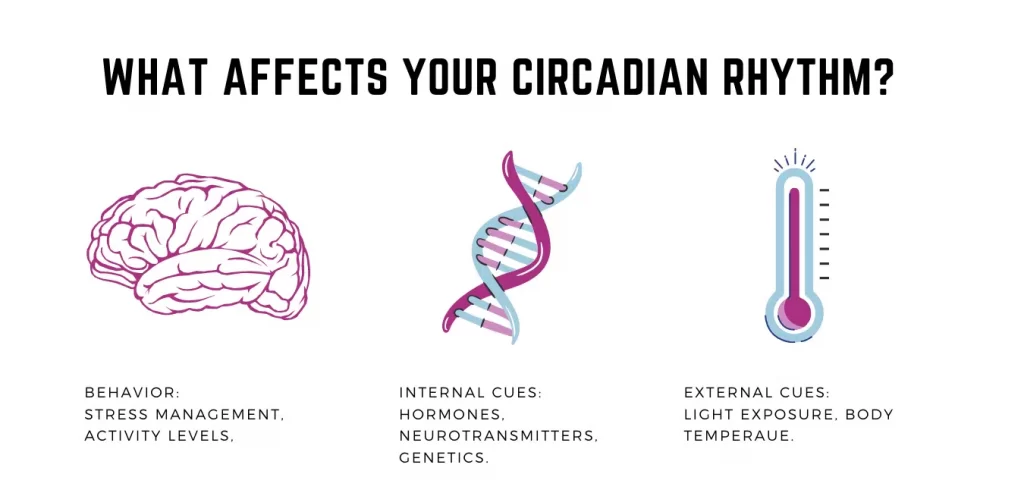
Work shifts.
Jet lags.
A lifestyle that encourages late-night hours or early wake times.
Screen time.
Medications you take.
Stress and pressure.
Mental health conditions.
Other Health conditions.
Poor sleeping habits.

1. Avoid blue light before bed: When your eyes are being exposed to blue light, it messes up the melatonin production in your body. So, it is best to avoid electronics before bed. If it is an impossible situation, you can also use blue-light-blocking glasses.
2. Sleep in total darkness: For a night of good quality sleep, it is best to sleep in complete darkness. You can also use blackout curtains or a sleep mask to get a night of quality sleep.
3. Spend time outside within 30 minutes of waking: Morning walks are the best way to get exposed to natural light. It is a great start to the day to wake up, get going, and have energy.
4. Bedtime and waking routine: It is essential to follow your sleep and waking routine on weekends also. The bedtime and waking time should not vary for more than one hour.
5. Avoid caffeine: Caffeine stimulates our nervous system and gives energy. So we should not consume caffeine in the late evenings.


One Comment